プロバイオティクスの活動を追跡するために作成されたツール; Tool created to track probiotic activity
Jan
7
2023年12月19日のThe Conversation記事によると、複数の研究によって裏付けられて いる500億ドルの米国のプロバイオティクス市場は、体内の有害な細菌や便秘を予防 し、コレステロールと血圧を下げ、ビタミン生成をサポートし、免疫システムを高める ことを示す。「2」 しかし、他の研究では、プロバイオティクスが特定の健康上の問題に対処するには限界 があることが強調されています。プロバイオティクスの効果を測定する方法はあります か?
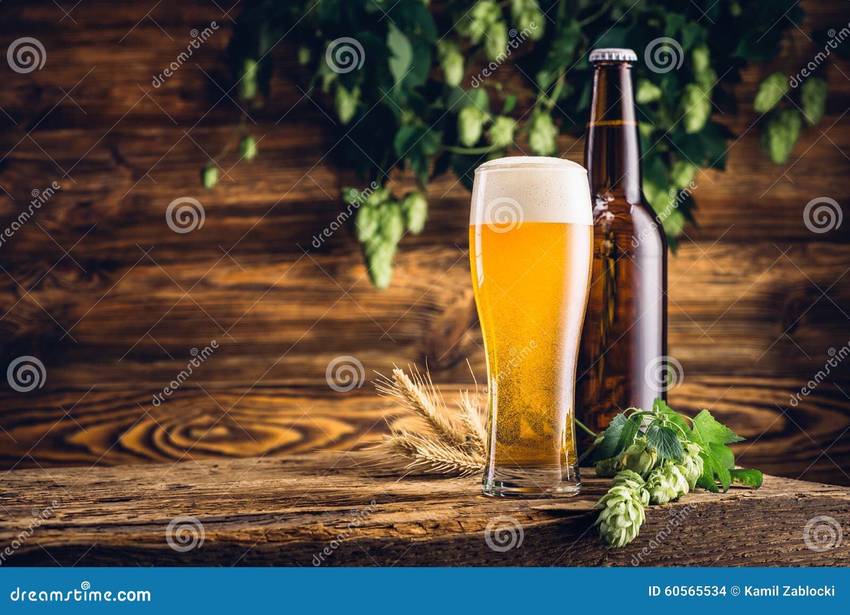
クレムソン大学のカルロス・ガルシアとジョージ・チュマノフは、酸化還元を通じて細 菌の代謝活動を検出する帯電したカーボン製のセンサーツールを作成しました。「2」 テストには、米国の店舗でテストツールを使用して広く販売されている人気のプロバイ オティクスヨーグルトとビールを使用しました。この検査では、乳酸菌、ビフィズス 菌、サッカロミセスなどの種の種類は区別されませんが、代謝活性のレベルが判定され ます。このツールを作成する前は、プロバイオティクスのモニタリングは大規模で費用 がかかりました。
The $50 billion US probiotics market is backed by multiple studies showing they prevent harmful bacteria in the body and constipation, lowers cholesterol and blood pressure, supports vitamin production, and boost the immune system, according to a December 19 2023 article in TheConversation.
However, other studies highlight the limitations probiotics have to address specific health issues. They are only as helpful as they are live active cultures. Is there a way to measure the efficacy of probiotics?
Clemson University’s Carlos Garcia and George Chumanov created a sensor tool from electrically charged carbon that detects the metabolic activity of bacteria through oxidation reduction, per the Conversation.
For testing, they used popular probiotic yogurt and beer, widely sold in U.S. stores using their test tool.
While the test does not distinguish the type of species such as Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium and Saccharomyces, it determines their level of metabolic activity. Before creating this tool, monitoring probiotics has been extensive and costly.