phenolic compounds in food aid in reducing free radicals; TCM dismissed by WebMD
Nov
11
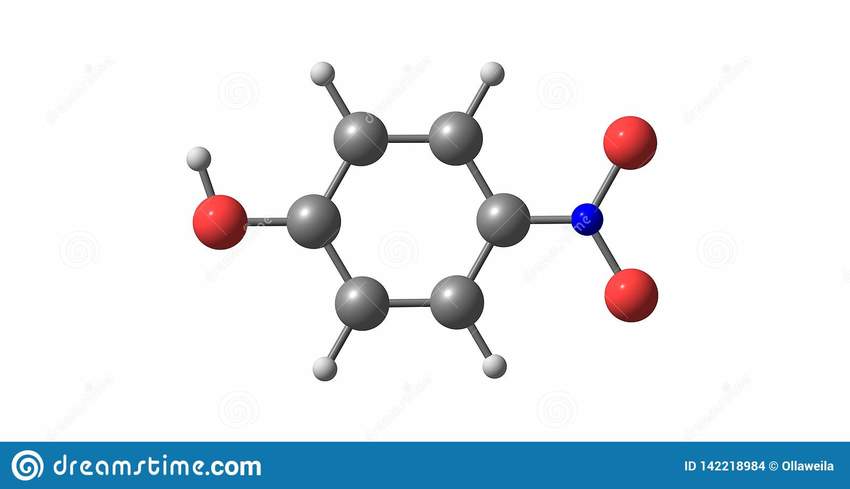
Phenolic compounds have received considerable attention for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic properties. Two main compounds mentioned here are protocatechuic acid (PCA) and protocatechuic aldehyde (PAL).
Phenolic compounds are naturally present in many plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, beans, spices, rice, crops, legumes, hemp, and lentils. Herbs such as basil, lemon thyme, and mint also contain high concentrations of these anti-oxidant compounds.
Salvia miltiorrhiza, also known as red sage, Chinese sage, danshen, is a perennial plant in the genus Salvia, commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine. While Danshen possesses high concentrations of PCA and PAL, WebMD warns that eating too much of it and for some people, it can cause upset stomach. On the other hand, WebMD fails to sight any scientific evidence or research it’s claims about Danshen while acknowledging that the same therapeutic compounds in other western foods are effective (2).
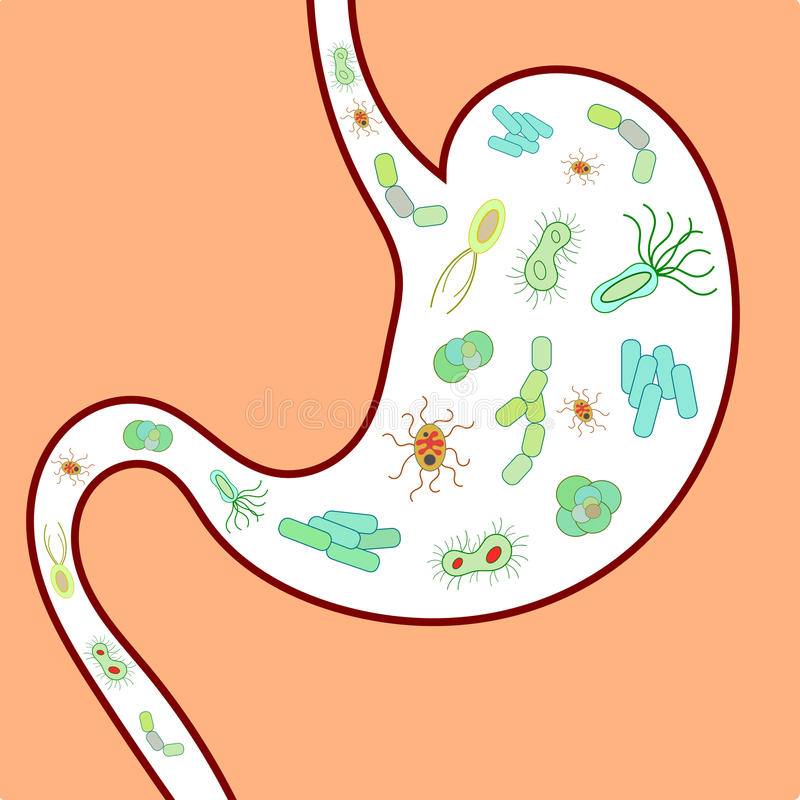
According to the Handawi article, the effectiveness of distributing these antioxidants to the body and brain depends in part on the gut microbiome ability to biotransform them into lower molecular weight compounds (1).
1. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2021/6139308/
2. https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-931/danshen